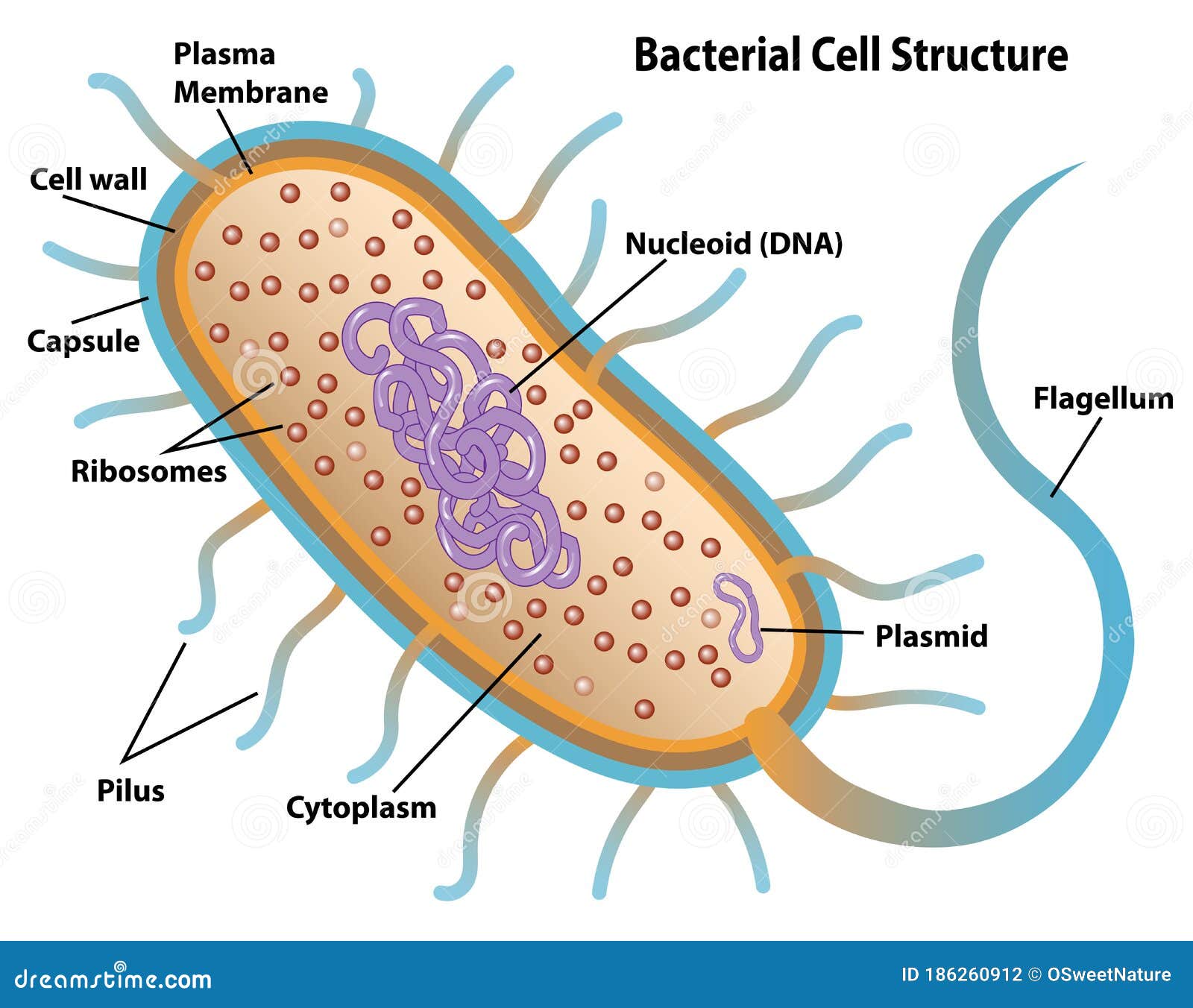
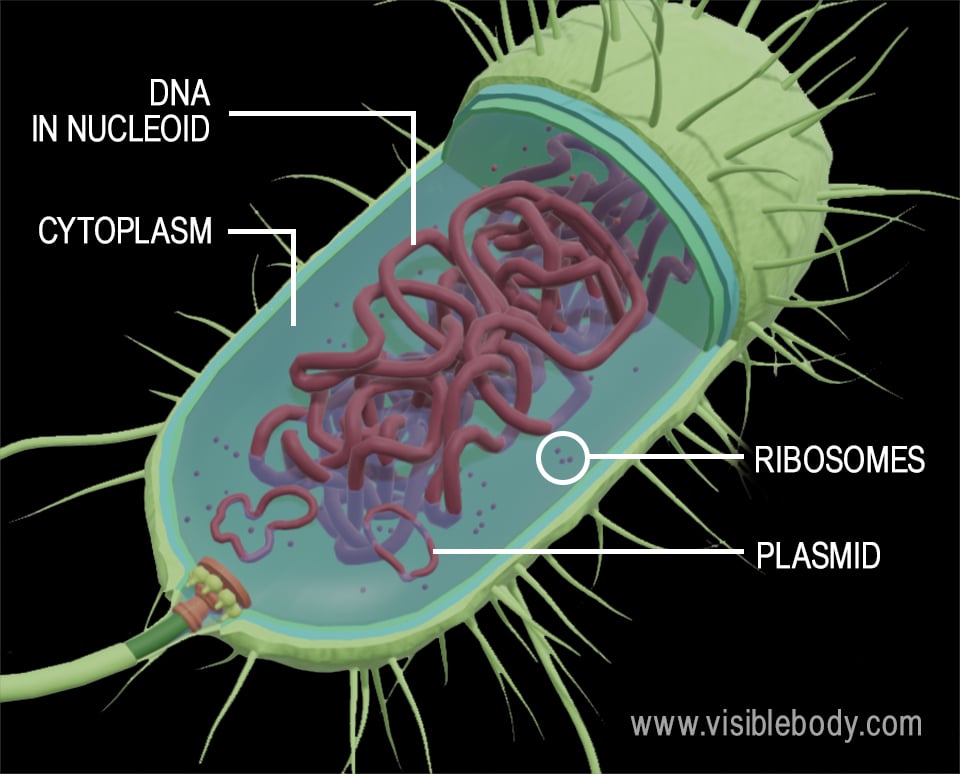
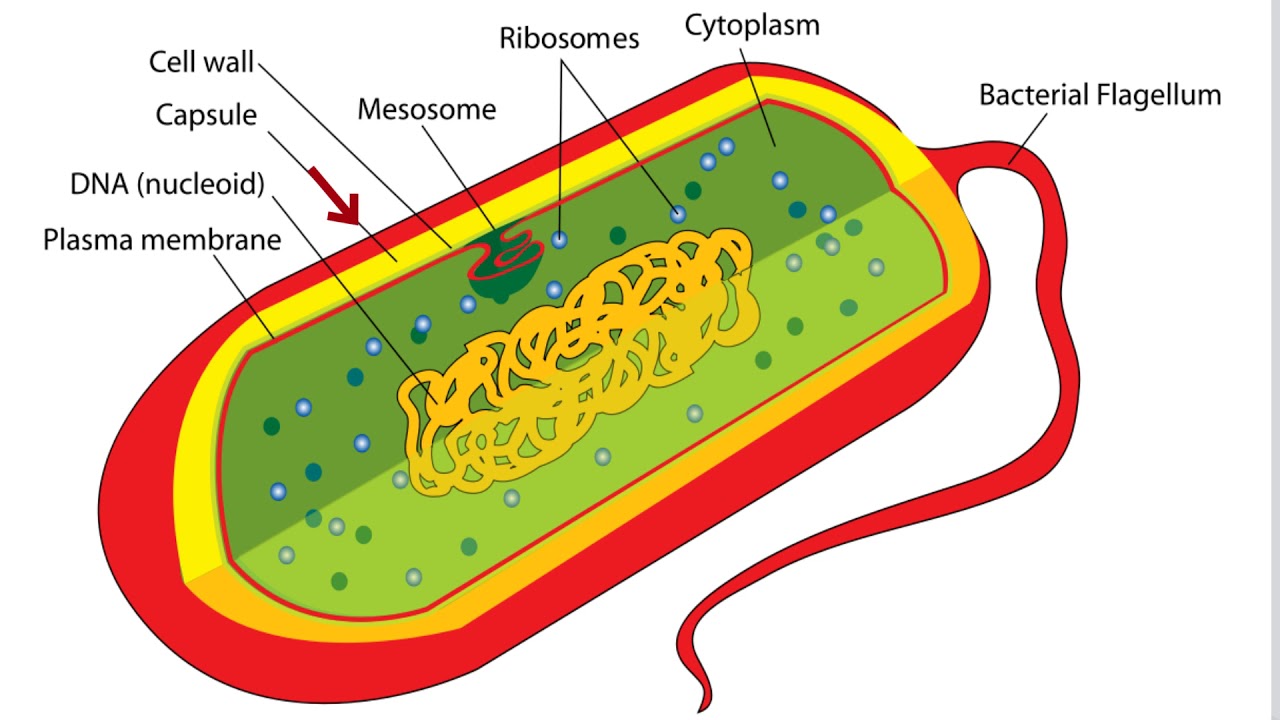
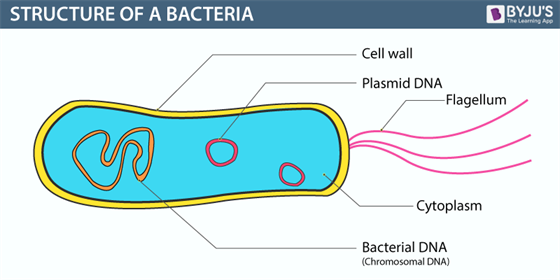
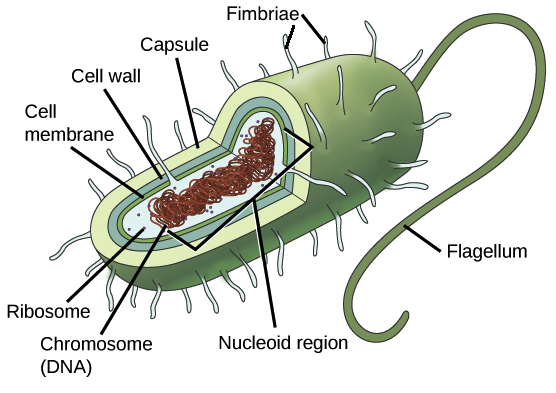
44 bacteria cell with labels
Gram Stain Technique - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Wipe the glass slide with spirit and wave the slide over the Bunsen burner to remove any unwanted microorganisms in the slide. Label one side of the glass slide with 1. Your initials 2. The date While flaming the inoculation loop be sure that each segment of metal glows orange/red-hot before you move the next segment into the flame. Studying predatory behavior in the bacterial kingdom Killing initiated with pinpoint accuracy Images with fluorescently labeled proteins showed that the protein secretion systems accumulate in the M. xanthus cell exactly at the contact site between...
Living material assembly of bacteriogenic protocells | Nature the fluorescence labels show e. coli -derived egfp (green) within the protocell interior and a continuous membrane of pao1-derived lipids (red) at the protocell surface. d, corresponding filtered...
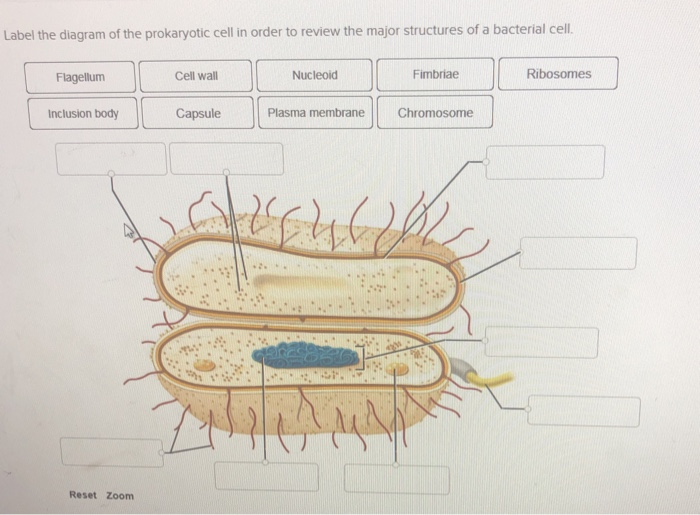
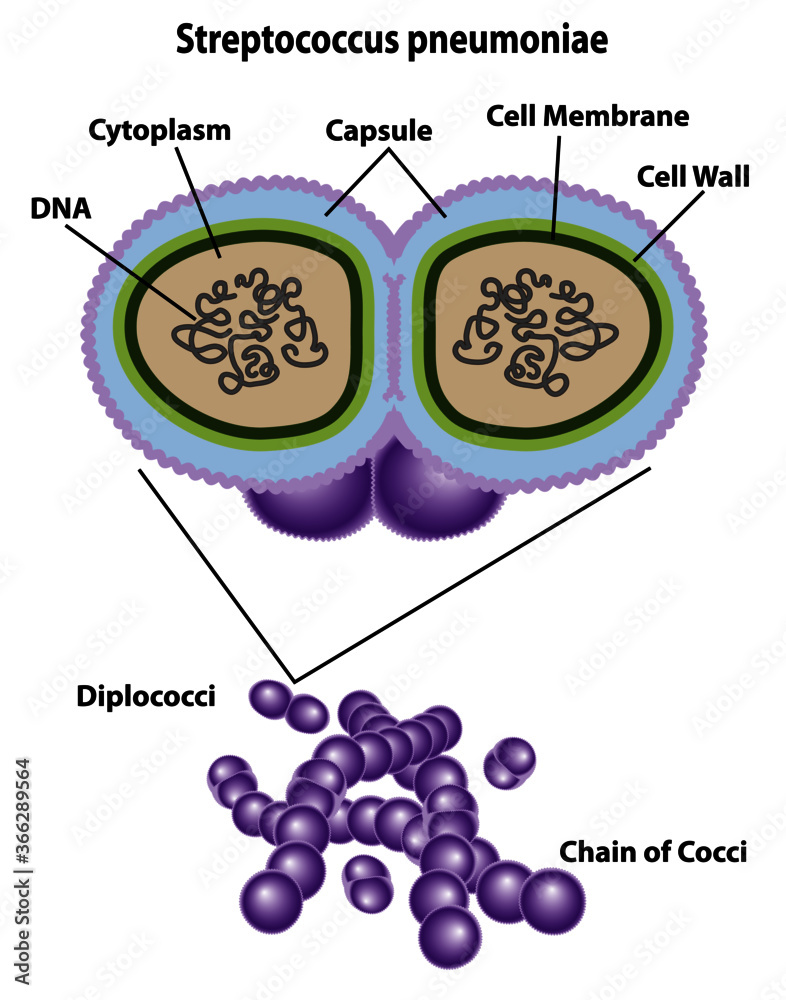
Bacteria cell with labels
An ADP-ribosyltransferase toxin kills bacterial cells by modifying ... The H1-T6SS is the most characterized and is thought to function as a strictly bacteria-targeting pathway. By contrast, the H2- and H3-T6SSs have been implicated in pathogenesis by functioning as virulence factors that target host cells and promote P. aeruginosa infection ( Bleves et al., 2014 ). Microscopic Morphology - BIO 2410: Microbiology - Baker College Eukaryotic microbes include protists, some fungi, and some flatworms (platyhelmintes) and roundworms (nematodes). The powerpoint file below introduces you to some of these Eukaryotic microbes. After reviewing the powerpoint file, see if you can identify the eukaryotic microbes in the fungi, protists, and helminth categories. Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
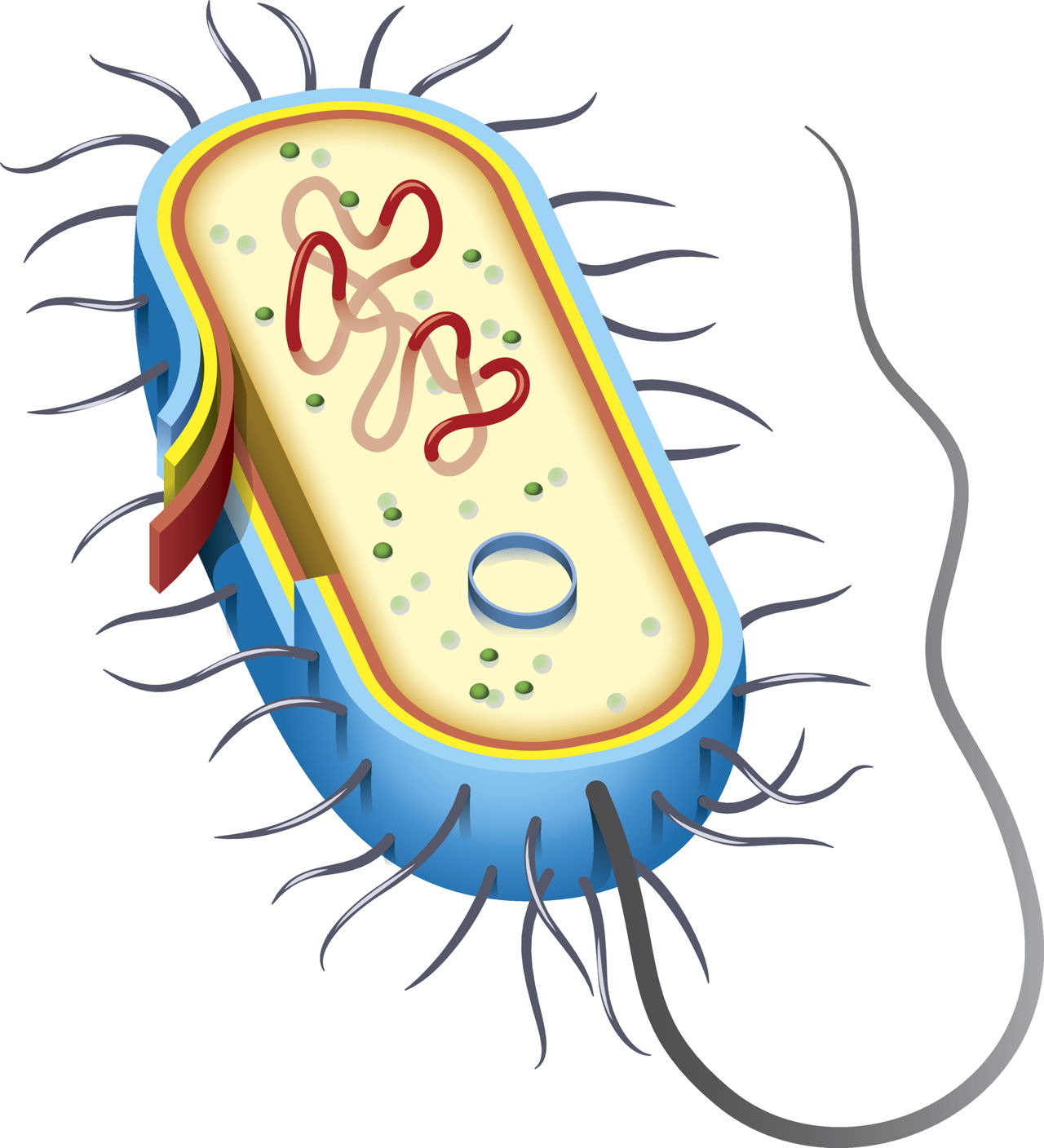
Bacteria cell with labels. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, structure and organelles | Kenhub There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. Streak Plate Method: Principle, Procedure, Uses - Microbe Online Remove the lid of the labeled agar plate just enough to insert the loop and lightly drag the loop with suspension in a zig-zag pattern in the top half of the T. (remember to stay within the region) Close the lid and flame the inoculating loop once again. Rotate the plate at 90° and remove the lid just like before just to fit to inoculating loop. Bacteria - Wikipedia Bacteria ( / bækˈtɪəriə / ( listen); singular bacterium, common noun bacteria) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Duke researchers identify chlamydia's stealthy cloaking device The mouse version of the bacterial inclusion was readily identified and labeled for destruction in human cells. "Chlamydia trachomatis is so good at evading our human responses," Coers said.
5 White Blood Cells Types and Their Functions - New Health Advisor Leukopenia is a low white blood cell count that can be caused by damage to the bone marrow from things like medications, radiation, or chemotherapy. Folate or vitamin B12 deficiency can also result in it. So can lymphoma, in which cancer cells take over the bone marrow, preventing the release of the various types of white blood cells. bacteriophage | Definition, Life Cycle, & Research | Britannica bacteriophage, also called phage or bacterial virus, any of a group of viruses that infect bacteria. Bacteriophages were discovered independently by Frederick W. Twort in Great Britain (1915) and Félix d'Hérelle in France (1917). D'Hérelle coined the term bacteriophage, meaning "bacteria eater," to describe the agent's bacteriocidal ability. Biosafety Cabinets- Definition, Classes (I, II, III) and Types Biosafety Cabinets (BSCs) are enclosed workspaces with a ventilated hood that is designed to contain pathogenic microorganisms during microbiological processes. The primary purpose of biosafety cabinets is to protect the laboratory personnel and the environment from the pathogenic microorganism as aerosols might be formed during the processing ... How to Create 3D Plant Cell and Animal Cell Models for ... - Owlcation Step 1: Choose Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell First and foremost, you must decide whether you will create a plant or animal cell. Plant cells and animal cells are shaped differently and contain different parts. The best way to decide? Take a look at some cell diagrams on an interactive site like Cells Alive.
Research team investigates the caterpillar-like bacteria crawling in ... Confocal microscope image of the caterpillar-like bacterium Conchiformibius steedae, up to 7 µm long, incubated with fluorescently labeled cell wall precursors to follow its cell growth. Chlamydia's stealthy cloaking device identified The mouse version of the bacterial inclusion was readily identified and labeled for destruction in human cells. "Chlamydia trachomatis is so good at evading our human responses," Coers said. Microscope, Microscope Parts, Labeled Diagram, and Functions Microscopes magnify or enlarge small objects such as cells, microbes, bacteria, viruses, microorganisms etc. at a viewable scale for examination and analysis. Microscopes consist of one or more magnification lenses to enlarge the image of the microscopic objects placed in the focal plane. The magnification power of simple laboratory microscope ... A RORγt+ cell instructs gut microbiota-specific Treg cell ... Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE)-labelled transferred T cells exhibited robust proliferation by day 3 in colon-draining C1 mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) of wild-type mice, with...
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm.
Cyanobacteria - Wikipedia Cyanobacteria ( / saɪˌænoʊbækˈtɪəri.ə / ), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria [4] that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name cyanobacteria refers to their color (from Ancient Greek κυανός (kuanós) 'blue'), [5] [6] which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae.
Gram Stain Technique (Theory) : Microbiology Virtual Lab I ... Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall which is made up of peptidoglycan (50-90% of cell wall), which stains purple. Peptidoglycan is mainly a polysaccharide composed of two subunits called N-acetyl glucosamine and N-acetyl muramic acid. As adjacent layers of peptidoglycan are formed, they are cross linked by short chains of ...
Bacteria - Genome.gov Bacteria are small single-celled organisms. Bacteria are found almost everywhere on Earth and are vital to the planet's ecosystems. Some species can live under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure. The human body is full of bacteria, and in fact is estimated to contain more bacterial cells than human cells.
Bacterial Capsule: Importance, Capsulated Bacteria Bacterial capsules can be visualized by light microscopy using special staining methods. If the layer is too thin to be seen by light microscopy it is termed a microcapsule. It is called the slime layer if it is so abundant that many cells are embedded in a common matrix. Capsule (also known as K antigen) is a major virulence factor of bacteria.
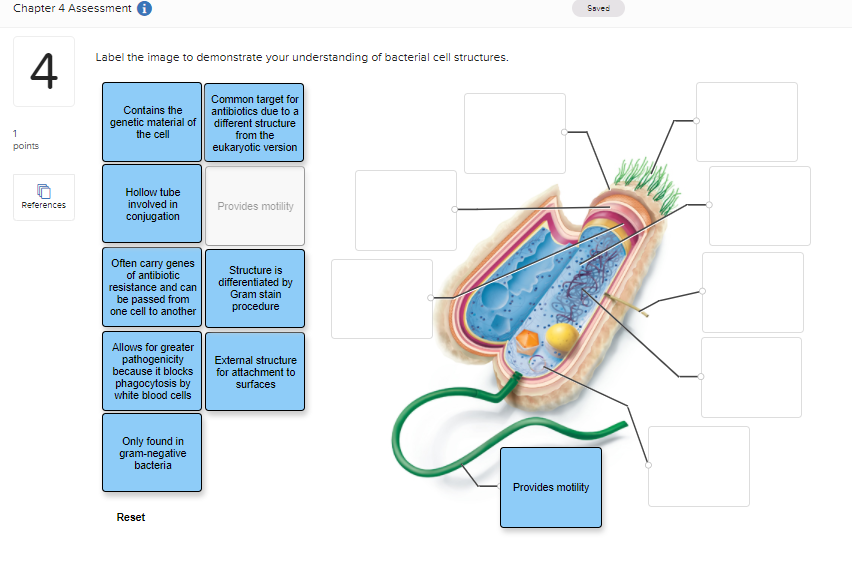
Do Bacteria Have Cell Walls - maxim-yersblogbest.blogspot.com Home Bacteria Do Bacteria Have Cell Walls MT_Emery.476 September 13, 2022 Structures External To The Cell Wall Prokaryotic Cell Cell Wall Bacterial Cell Structure
Bacteriology Notes - Microbe Notes Bacteriology. Bacteriology is a branch or discipline of science that studies different characteristics of bacteria and their association with other organisms or disciplines. Over the years, the discipline of bacteriology has evolved from the microbiological tests performed only by physicians, the application of the germ theory of disease and ...
Penicillins: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health The list of gram-positive bacteria that are treatable by penicillins includes those of the Clostridium, Listeria, Neisseria, Staphylococcal, and Streptococcal genus. 8 Natural penicillins—penicillin G and penicillin V—are still used today and are appropriate for the treatment of certain common and uncommon bacterial infections.
List of bacteria genera - Wikipedia This article lists the genera of the bacteria.The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However many taxonomic names are taken from the GTDB release 07-RS207 (8th April 2022).
The cell: Types, functions, and organelles - Medical News Today People tend to consider the Golgi apparatus the post office of the cell, where items go through packaging and labeling. Once materials leave, they may be useful inside or outside the cell....
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
Microscopic Morphology - BIO 2410: Microbiology - Baker College Eukaryotic microbes include protists, some fungi, and some flatworms (platyhelmintes) and roundworms (nematodes). The powerpoint file below introduces you to some of these Eukaryotic microbes. After reviewing the powerpoint file, see if you can identify the eukaryotic microbes in the fungi, protists, and helminth categories.
An ADP-ribosyltransferase toxin kills bacterial cells by modifying ... The H1-T6SS is the most characterized and is thought to function as a strictly bacteria-targeting pathway. By contrast, the H2- and H3-T6SSs have been implicated in pathogenesis by functioning as virulence factors that target host cells and promote P. aeruginosa infection ( Bleves et al., 2014 ).




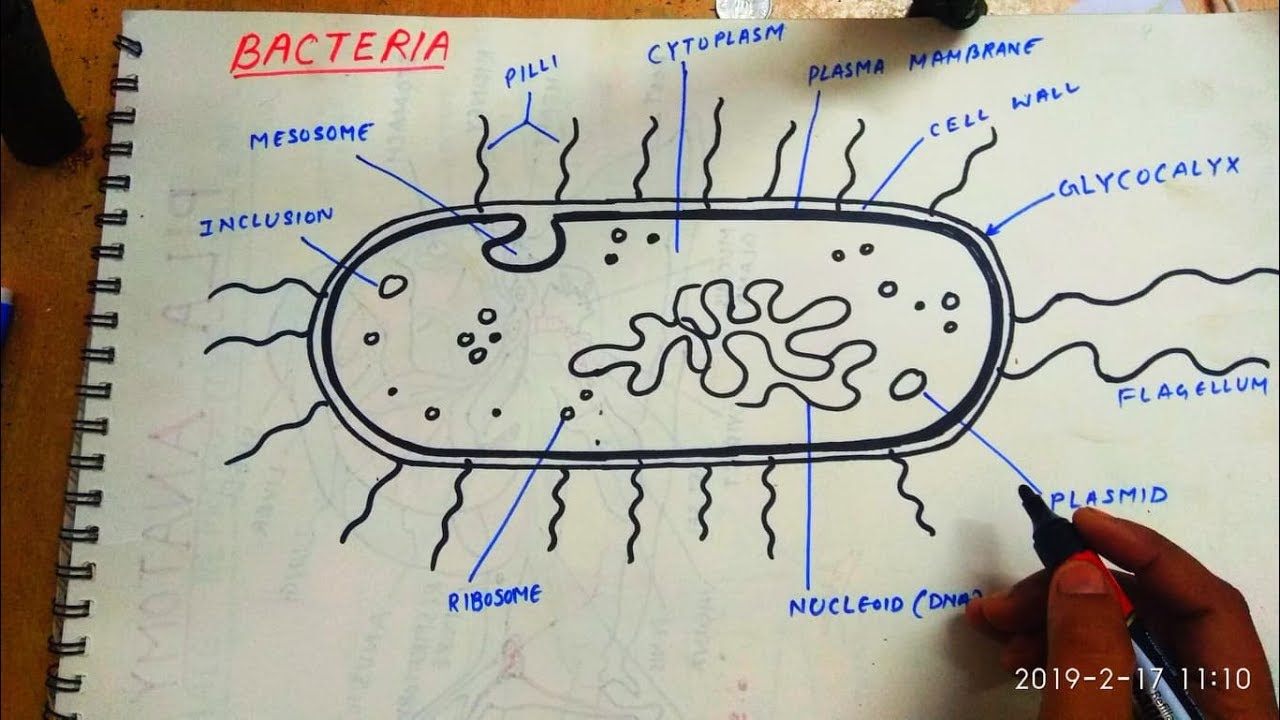
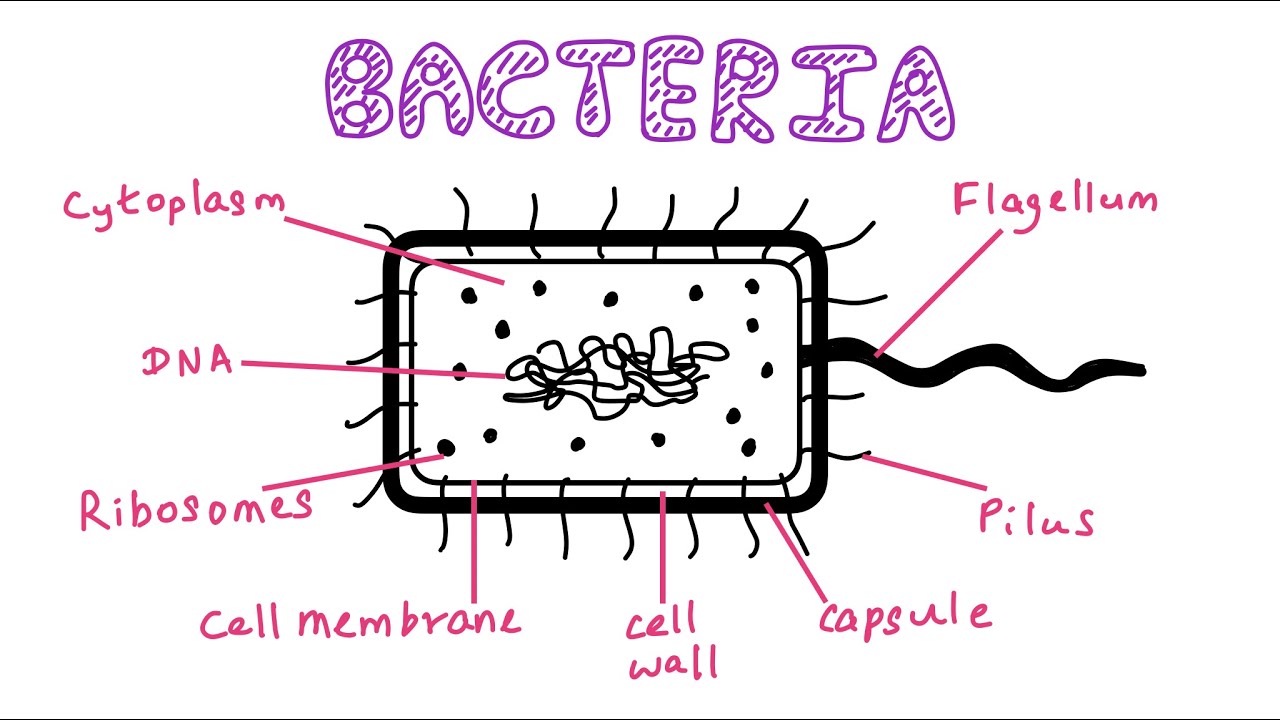
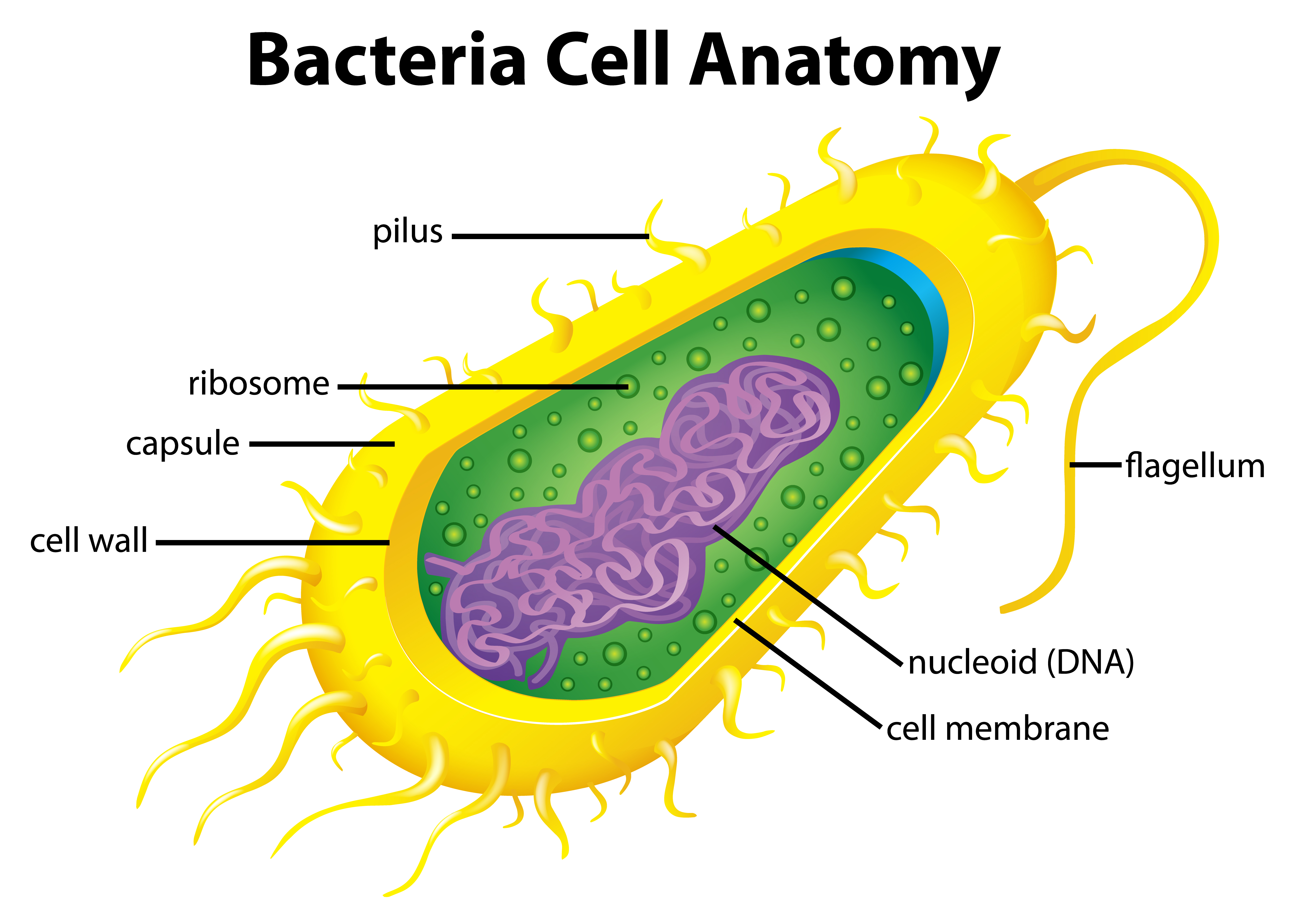


/shigella-bacteria--illustration-758308491-5a02252f9e9427003c1759be.jpg)






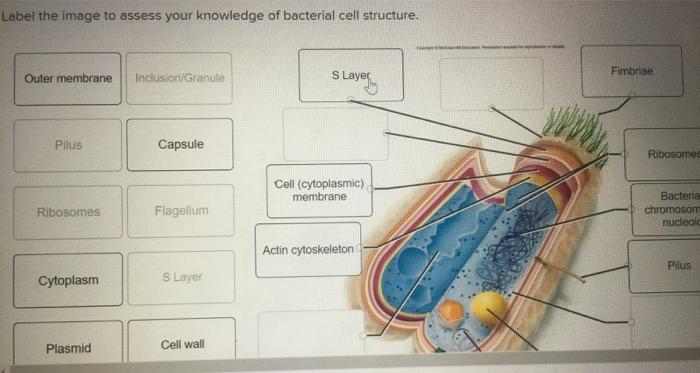



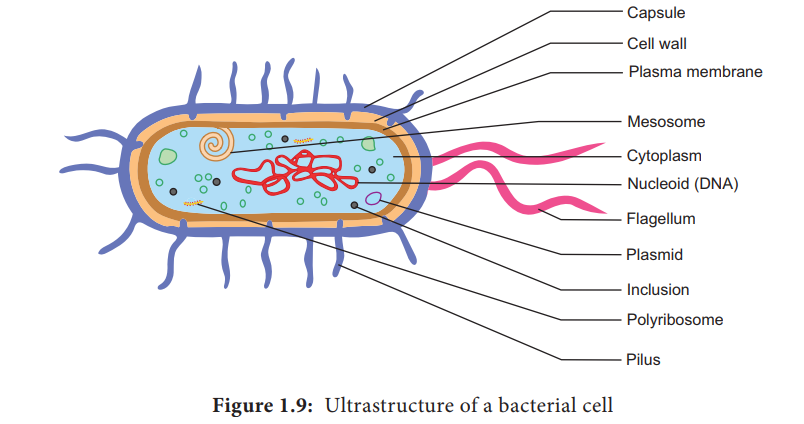
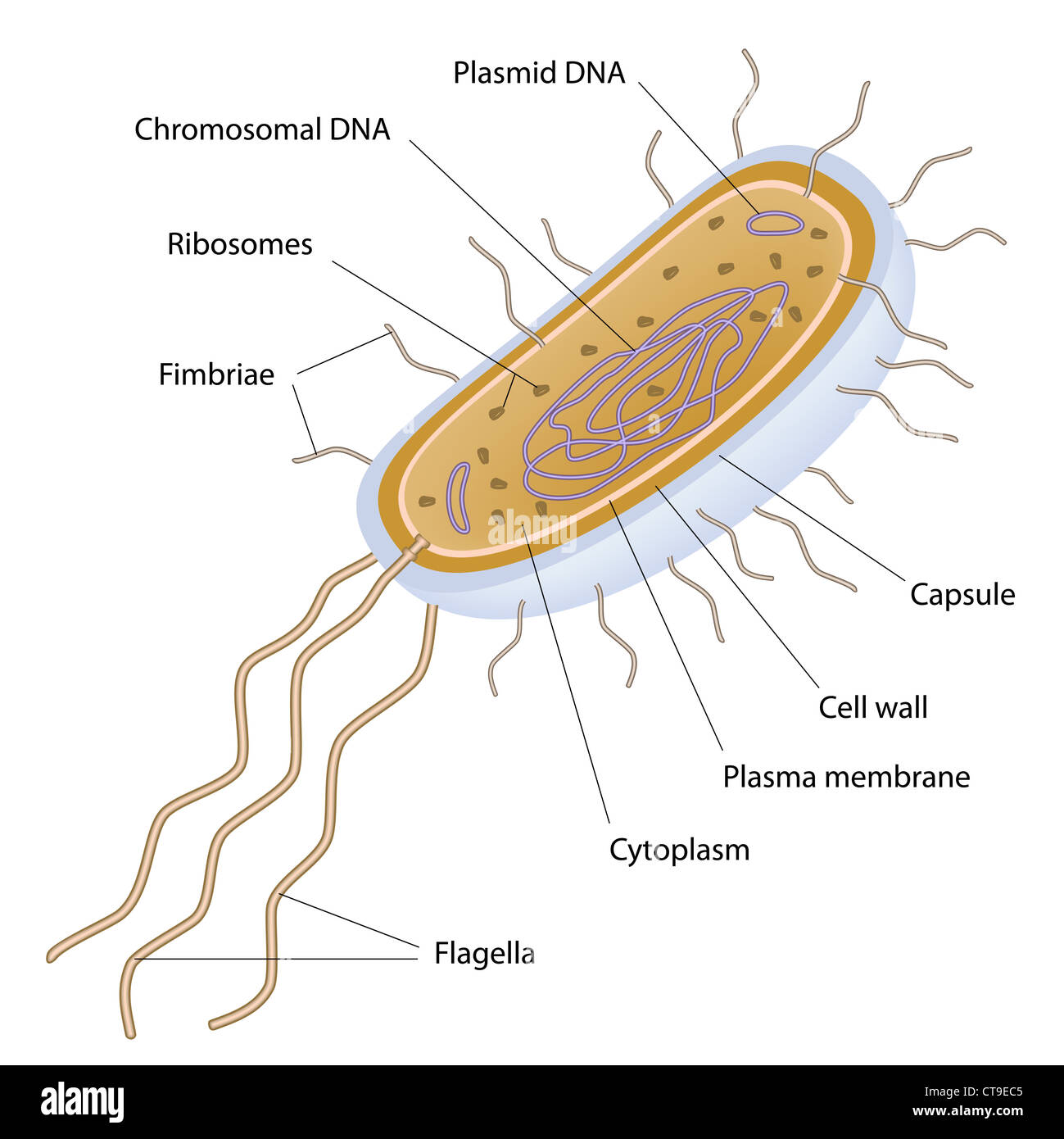



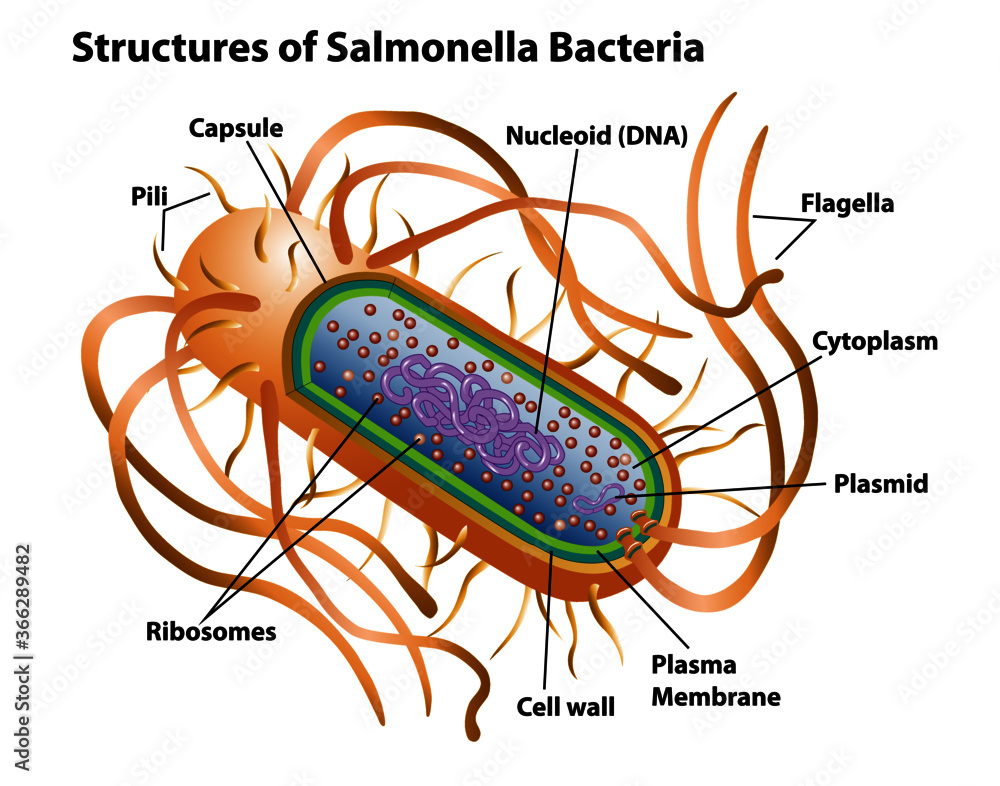



Post a Comment for "44 bacteria cell with labels"